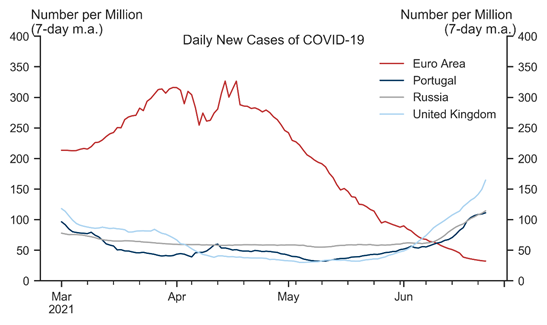
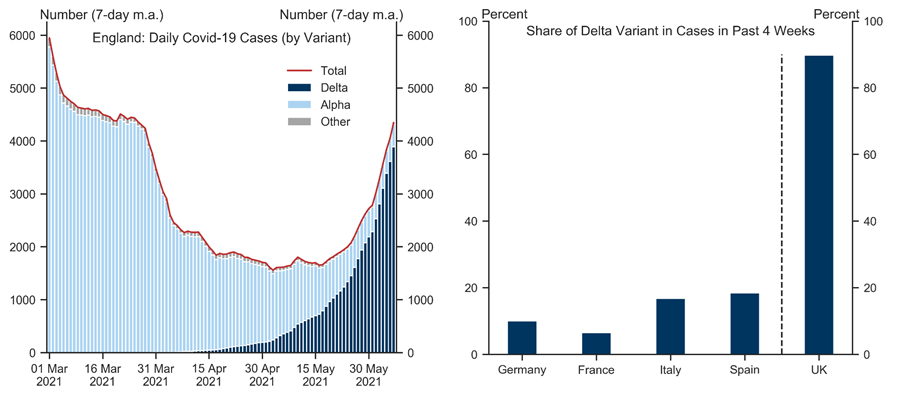
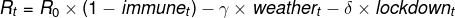The spread of the delta variant across Europe has raised concerns that a renewed wave of infections could slow the reopening and weigh on the Euro area economic outlook. Using a simple framework motivated by standard epidemiological models, we jointly analyse the scope for renewed outbreaks in the presence of ongoing mass immunisation, mitigation measures, and weather effects. While uncertainty is high, our analysis suggests there is a risk of rising infections in the Euro area later in the summer and into the winter months, given the high transmissibility of the delta strain.
That said, our analysis suggests that the risk of strong upward pressures on Covid hospitalisations has fallen sharply given high and steadily rising levels of collective immunity across Europe. Assuming policymakers remain primarily focused on limiting hospitalisations, we therefore think the delta variant poses a manageable risk to the reopening and our constructive view on the European recovery.
The Delta Variant—A Manageable Risk
The Risk of Large Outbreaks
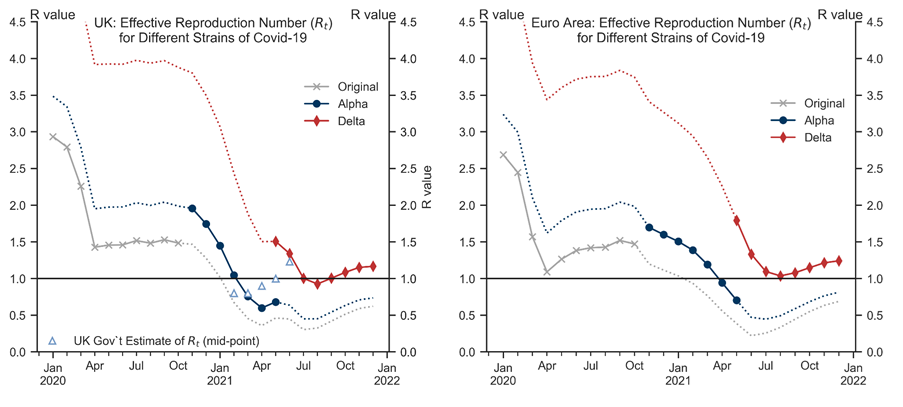
R0: Using external estimates, we assume that the basic reproduction number is 2.6-2.9 for the original strain, 3.2-3.5 for the alpha variant, and 5.0-5.5 for the delta variant, with the higher values applicable to the UK;[4]
immunet: Our Global team's vaccination timelines, combined with (fairly conservative) assumptions on natural immunity from past infections, yield paths for the share of immune population;[5]
𝛿 and lockdownt: In our previous work, we have estimated the effect of lockdowns on R, hence we set 𝛿 = 0.017 and assume the path for lockdown easing, lockdownt, that is the same as in our growth forecasts;
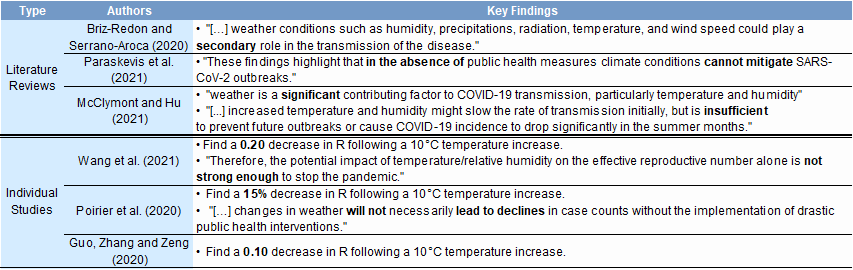
γ and weathert: We assume that a 10-degree Celsius increase in temperature lowers R by 0.15 (a mid-point of the studies shown in the Appendix).[6]
Parameter uncertainty: While we have tried to calibrate the three parameters (R0, 𝛿, and γ) using both external estimates and our previous work, there is large uncertainty around each of them. For example, the values of R0 may differ across countries (e.g. due to different population density) and there are wide ranges in the literature for each of the three strains. Changing this parameter for a particular strain would shift the corresponding line shown in Exhibit 3 up or down.
Linear specification: Our previous work suggests lockdown measures may have non-linear effects on R (for simplicity, we assume this away here). Moreover, voluntary social distancing and other behavioural factors (e.g. mask wearing) may also affect R. Insofar as people remain more cautious, that could additionally push down on R going forward relative to our results in Exhibit 3.
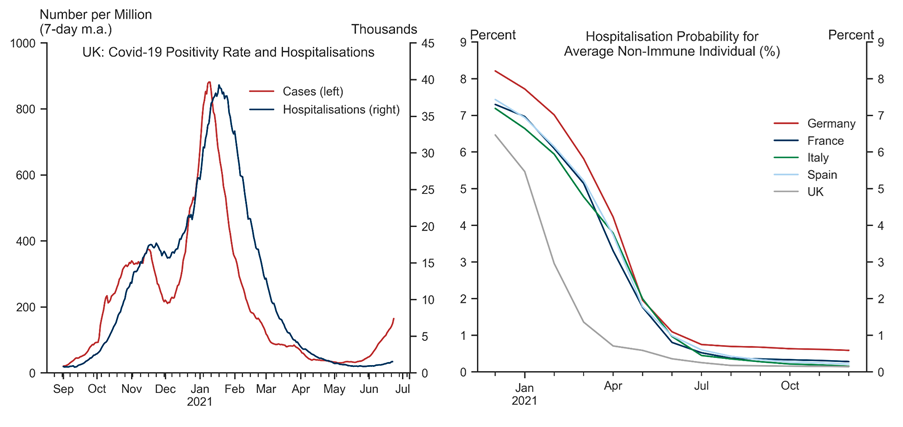
The Risk of Hospital Overflow
Nikola Dacic
- 1 ^ A caveat to this is that the amount of genome sequencing differs across countries, with more sequencing in the UK than in many other European countries, which could lead to an understatement of the prevalence of the delta strain in new cases in those countries.
- 2 ^ See, for example, equation (3.2) in Shaw and Kennedy (2021).
- 3 ^ See also "Lockdowns in SIR Models" by Benjamin Moll, May 2020.
- 4 ^ We calibrate the R number of the original strain to 2.9 in the UK and 2.63 in the Euro area following two respective studies (here and here). We assume the alpha strain has an R number that is 6-tenths higher than that of the original strain (see here). We assume the delta variant has an R that is 60% higher than that of the alpha variant (so equal to 5)—see here and here.
- 5 ^ Although our assumptions on natural immunity from past infections are fairly conservative, we do assume 'cross-variant' immunity. In other words, past infections with strains other than the delta strain are assumed to provide some immunity against the delta strain. Assuming away this form of natural protection against the delta variant would tend to raise the R number schedules shown in Exhibit 3 for the delta variant.
- 6 ^ A recent study by professors at Yale University has found that 17.5% of the virus' reproductive number was attributable to meteorological factors—implying potentially more significant effects of the climate than we assume here (additionally, we only focus on the temperature, and ignore factors such as humidity or radiation during the year).
- 7 ^ See, for example, a study from Public Health England, which estimates vaccine efficacy against hospitalizations at 94% after dose 1 and 96% after dose 2 for the Pfizer vaccine, and 71% after dose 1 and 92% after dose 2 for the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine. By contrast, another study from Public Health England estimates vaccines efficacy against symptomatic disease at 33% after dose 1 and 88% after dose 2 for the Pfizer vaccine, and 33% after dose 1 and 60-67% after dose 2 for the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine.
- 8 ^ This simplifying assumption is a proxy for the actual distribution process for vaccines across Europe.
- 9 ^ We obtain the age-specific hospitalisation rates from the "COVID-19 surveillance report" by the ECDC, available at https://covid19-surveillance-report.ecdc.europa.eu/. For simplicity, we assume these are identical across countries.
- 10 ^ For example, nearly 90% of hospital beds in England were reported to be full in mid-December last year as the alpha variant was spreading rapidly.
Investors should consider this report as only a single factor in making their investment decision. For Reg AC certification and other important disclosures, see the Disclosure Appendix, or go to www.gs.com/research/hedge.html.