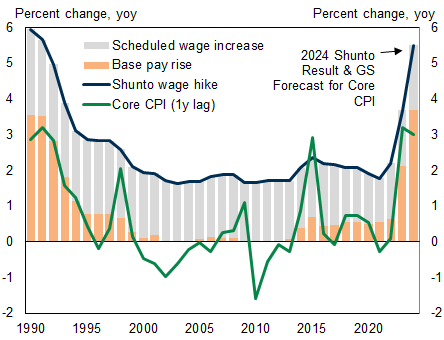
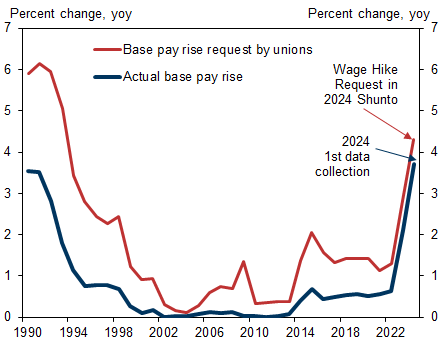
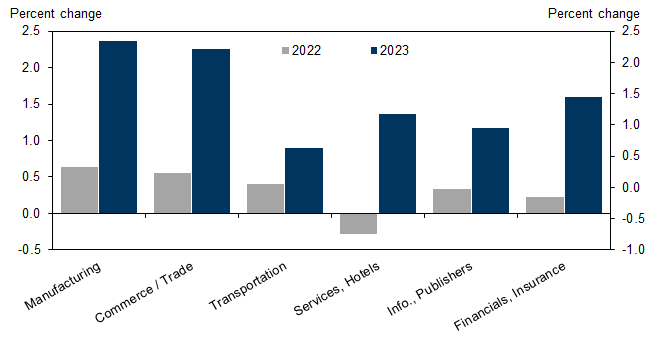
According to the initial shunto wage increase data for agreements between labor unions and companies, the base pay rise for 2024 is 3.7%, well above last year’s final figure of +2.1%. Headline wage growth, including scheduled wage hikes, is 5.3% (2023 final: 3.6%).
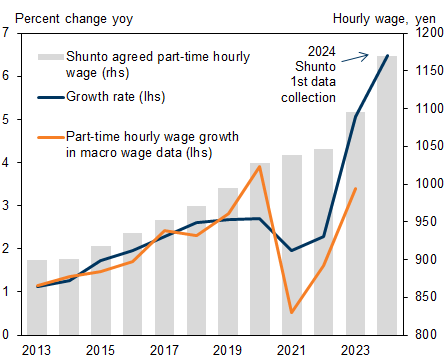
The data also show an increase in part-time hourly wages of 6.5%, exceeding last year’s already strong growth of 5.1%.
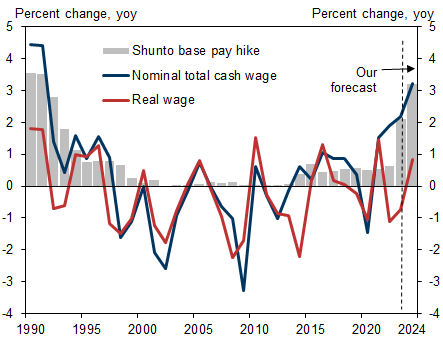
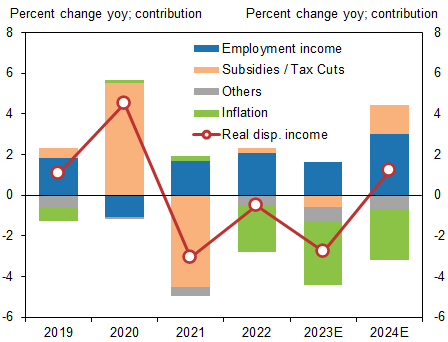
We raise our 2024 estimate for shunto base pay hike to 3.2% from 2.5% in view of the strong shunto results so far. If this is realized, we estimate that overall macro wage growth, including bonuses and part-time wages, will rise 3.2% in FY2024. Real disposable income would rise 1.2% (previous forecast +0.8%).
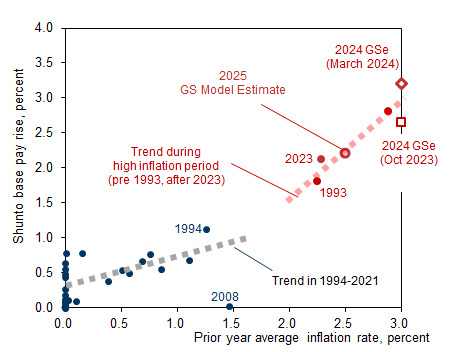
The high base pay rise in the 2024 shunto reaffirms the relationship that in a high inflation period of more than 2%, wages respond more strongly to price rises. Based on our CPI forecast of 2.5% for 2024, our model implies shunto base pay rise of 2.2% in 2025, suggesting a strong possibility of achieving over 2% base pay for three straight years.
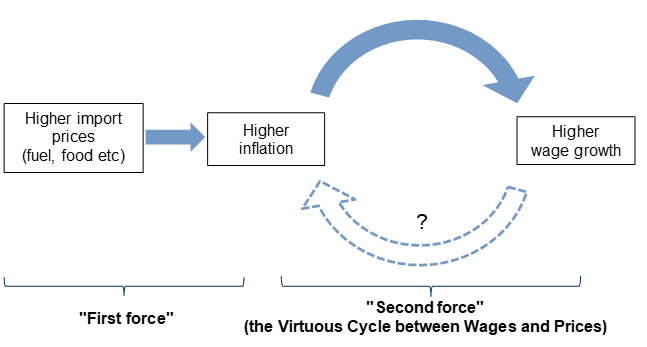
As such, the BOJ could deem an increase in the base pay rise in the 2024 shunto as an important factor in achieving a virtuous cycle between wages and prices as well as sustainable inflation.
First Data Release Indicates 3.7% Base Pay Rise, Above 3% Level for the First Time Since 1991
Exhibit 1: Shunto Wage Increases and Consumer Price Index
Exhibit 2: Shunto Wage Increase Requests and Actual Base Pay Rises
We Raise our Wage Growth Estimates to Reflect the Strong Shunto Wage Data
Exhibit 4: We Estimate Real Wage Growth above +1% in 2024
Exhibit 5: Real Disposable Income Finally Turning Positive in 2024
With the Base Pay Rise Likely to Remain Above 2% in 2025, Continuous Price and Wage Rises Increase the Likelihood of a Virtuous Cycle Between Wages and Prices
Exhibit 6: Base Pay Rise Reacts Strongly to Inflation During Periods of High Inflation Exceeding 2%
- 1 ^ The magnitude of revision to macro nominal overall wage growth is smaller compared to the upward revision to the shunto base pay hike. Explanations are, in addition to adjusting the boost from the strong wage hikes by the steel majors and incorporating the gap wage hike between large and smaller companies, (1) our real GDP forecast for 2024 is lower compared to October 2023 when we made our previous forecast, which lowers the contribution of bonus/overtime wage by 0.3pp, and (2) running rate of wage growth upto January has been slower than we assumed in October, which reduces the FY2023 outlook for a lower starting base for FY2024.
- 2 ^ Disposable income includes tax refunds and support for low-income households (total ¥5 tn), the bulk of which will be paid out by summer 2024. On the other hand, increase in personal income tax and social security contribution, accompanying wage growth, reducing disposable income.
- 3 ^ We estimate marginal propensity to consume based on yoy changes in real disposable income and real household spending for FY1994-FY2019. Our estimation results are broadly similar to those of the Cabinet Office (2010) and the Bank of Japan (2016).
- 4 ^ This estimate is derived from the following model. Shunto base pay rise = 0.23*** + 0.15** x previous year's core CPI + 0.64*** x high-inflation period dummy x previous year's core CPI + 0.08** x previous year's nominal labor productivity growth rate. All regression coefficients have a 1-period lag. The estimation period is 1992-2024. *** and ** are statistically significant at the 1% and 5% levels respectively. Our 2025 shunto model estimate assumes zero nominal labor productivity growth in 2024.
Investors should consider this report as only a single factor in making their investment decision. For Reg AC certification and other important disclosures, see the Disclosure Appendix, or go to www.gs.com/research/hedge.html.